Explore The Latest Advancements In Drone Innovations
UAV News Updates And Highlights
Stay Informed With The Latest Breakthroughs In Artificial Intelligence
Major Headlines And Key Stories In Artificial Intelligence
Iran's "Drone Carrier" Might Join Combined Exercises With Russia and China

Converted boxship Shahid Bagheri, Iran's "drone carrier"
The annual naval exercise known as the Iranian-Chinese and Russian Exercise Maritime Security Belt is traditionally held around mid-March, following a longstanding schedule.
In 2025, the Maritime Security Belt exercise is anticipated to include the departing Chinese Navy Group, which is close to finishing its six-month forward deployment at the PLA Navy’s Project 141 Overseas Support Base in Doraleh, Djibouti. The 46th Naval Escort Group, set to return, comprises the Type 052D destroyer Jiaozuo (D163), the Type-054A frigate Xuchang (F536), and the Type 903A supply ship Honghu (K963).
This 2025 drill will be their first collaborative exercise with allied navies as they make their way back to their homeport in Zhanjiang, Guangdong, where the South Sea Fleet of the PLA Navy is headquartered.
The Russian contingent likely includes the Steregushchiy Class Project 20380 missile corvettes, Hero of the Russian Federation Aldar Tsydenzhapov (F339) and Rezkiy (F343), along with the oiler Pechenga (IMO 7710977). As reported by the Pacific Fleet's Press Office through Izvestia, these vessels departed Vladivostok on February 3 to carry out missions in the Asia-Pacific domain. During their journey across the Sea of Japan, the fleet engaged in air defense maneuvers to counteract drone threats and conducted drills aimed at thwarting potential attacks from unmanned boats. This training could prove beneficial should any Iranian-backed Houthi forces in the Red Sea or Gulf of Aden mistakenly identify the Russian ships as hostile entities.
Although the Pechenga is traveling with its AIS automatic identification system turned off, it's known that the flotilla reached the waters off Bali by February 15 to participate in Exercise Komodo-2025 alongside the Indonesian Navy.
The visibility of Iranian naval forces in the exercise, representing both the IRGC (Nedsa) and the regular Navy (Nedaja), will become clearer as the event approaches and will depend on the operational status of their vessels, a perennial challenge given the aging state of the Iranian fleet. Nevertheless, the exercise is expected to include drone and missile launches, reflecting Iran's current strategic focus.
This may offer Nedsa a chance to prove the operational effectiveness of their new drone carrier, Shahid Bagheri (C110-4), which was last observed at its usual anchorage near Bandar Abbas on a clear February 1st. Some media reports have depicted Nedsa's promotional footage of a small, jet-powered, one-way attack drone, resembling a model aircraft, taking off from the Shahid Bagheri, as a significant change in maritime power dynamics that could alarm Israel.
While the feasibility of these one-way drone launches is recognized, the vessel is also capable of deploying missiles, helicopters, and fast attack boats, similar to any standard frigate. However, there is yet no evidence that a fixed-wing aircraft could land on Shahid Bagheri’s 180-meter flight deck, considering the challenges posed by the off-center flight deck’s pitch and roll and the air turbulence generated by the ship's towering stern.
Outside of stable peacetime conditions, the survivability of this 20-year-old converted tanker in conflict situations, or even during heightened tensions, would likely be brief, potentially lasting hours rather than days. Despite its robust Korean build, a ship surveyor might have deemed the Perarin more suitable for scrap than transformation into the Shahid Bagheri, now the flagship of the Nedsa fleet.

A Person Unable To Move Has Mastered The Ability To Operate A Virtual Drone Using Only Their Thoughts, Thanks To A Brain Implant.
A revolutionary brain implant has empowered a 69-year-old man with paralysis to pilot a virtual drone solely with his thoughts. Scientists claim that this degree of accuracy and liberty in virtual navigation has not been achievable in the past. This surgical device can identify and interpret the fingers the paralyzed individual intends to move, enabling him to steer a quadcopter within a specially crafted video game.
Globally, millions endure severe physical disabilities, and training with such brain implants is increasingly recognized as a promising approach to restoring mobility.
Although current instances of the technology have difficulty interpreting intricate motions that individuals with paralysis wish to execute, such as the movements of separate fingers, if these exact motions could be revived through therapy, they might gradually relearn how to engage in tasks like typing or playing musical instruments.
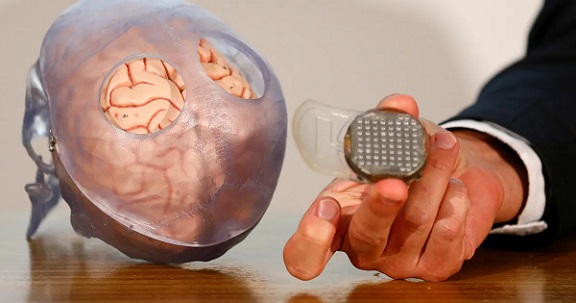
In a recent investigation featured in the journal Nature Medicine, researchers engineered a brain implant that empowers a participant to fly a drone using their own commands. The device was inserted into the individual's left precentral gyrus, the area of the brain that governs hand movement control.
This implant continuously monitors the electrical activity of neurons in the brain, focusing on patterns associated with intricate physical actions. Scientists tracked the pattern of nerve cell activity in the participant while he watched a virtual hand execute different motions. Using artificial intelligence algorithms, they then pinpointed the brain signals that corresponded to particular finger movements.
Researchers have discovered that these cues can direct the AI system to precisely anticipate the participant's intended finger movements. Utilizing this data, they enabled the participant to manipulate three separate groups of fingers, including two-dimensional movements of the thumb, in a digital hand. Experts claim that this degree of movement accuracy and autonomy was not achievable before.
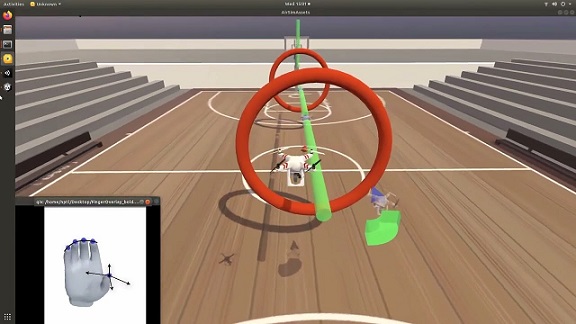
Researchers have broadened the use of virtual finger manipulation to include controlling a quadcopter in a video game. Movements of the fingers, interpreted by a brain implant, were used to adjust the speed and navigate the direction of a quadcopter within the game. The implant enabled the individual to steer the drone through various barriers, including flying it through rings that appeared unexpectedly in the game.
"Using precise motor control for iBCI-operated video games can address the unfulfilled needs of individuals with paralysis," the researchers stated. “The participant conveyed or showed a feeling of empowerment, enjoyment, and social engagement, addressing numerous unmet needs of individuals with paralysis,” they remarked.
This recent breakthrough might result in improved implants that assist paralyzed individuals in controlling on-screen cursors, potentially opening up more sophisticated online capabilities such as emailing, browsing through social media feeds, or watching streaming content.

Stay informed with the most recent advancements in drone technology, an ever-evolving field that continues to push the boundaries of what unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) can achieve. From cutting-edge developments in drone design and functionality to remarkable improvements in battery life and autonomous navigation, there is much to discover.
For instance, recent statistics indicate a significant increase in the use of drones across various industries, including agriculture, where drones help monitor crop health and optimize yields. Additionally, the transportation sector is seeing a rise in drone delivery systems, promising faster and more efficient parcel delivery. Keep up with these exciting trends and more by following UAV News Highlights on NewsNow.
Drone technology is advancing at a rapid pace, driven by increasing demand and technological innovation. In the realm of design, engineers are experimenting with more aerodynamic forms and lightweight materials, which enhance flight efficiency and extend operational range. Innovations in battery technology are equally impressive, with new lithium-sulfur and solid-state batteries offering longer flight times and shorter charging cycles, enabling drones to perform more extended missions without frequent interruptions.

Autonomous navigation systems are becoming increasingly sophisticated, employing artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms to enable drones to make real-time decisions during flight. This capability is transforming industries such as agriculture, where UAVs equipped with multi-spectral sensors can analyze plant health, detect pests early, and even apply precise amounts of fertilizer, thus maximizing productivity while minimizing waste.
Moreover, the logistics and transportation sectors are on the brink of a revolution, thanks to drone delivery systems. Companies like Amazon and UPS are piloting drone fleets to deliver packages directly to consumers' doorsteps, reducing delivery times from days to mere hours, especially in urban areas. This innovation not only enhances customer satisfaction but also reduces carbon emissions by decreasing reliance on traditional delivery vehicles.
With these advancements, drones are becoming essential tools for various applications, from disaster relief efforts, where they provide crucial aerial imagery and deliver medical supplies, to environmental monitoring, where they track wildlife and assess natural habitats. Stay ahead of these developments and more by keeping up with UAV News Highlights on FrizeMediaTech, ensuring you never miss out on the latest breakthroughs in this dynamic technological landscape.

Tweet








New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave a comment in the box below.