What Causes Diabetes
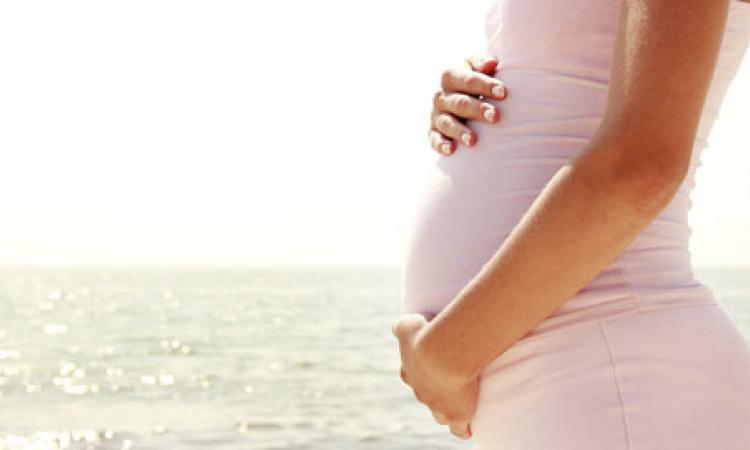
Achieving Healthy Pregnancy Despite Diabetes
What causes diabetes: Among diabetic pregnant women, the most common problem when it comes to their baby's health is the condition called "macrosomia" or having a baby with large body. This is because the blood of the mother with diabetes is interchanged with that of the baby inside the womb. Insulin is a hormone that is produced by your pancreas, and is essential to move glucose (or sugar) into your cells after your body breaks down food for energy. In the course of pregnancy, your body becomes less sensitive to the effects of insulin, which can lead to what’s known as gestational diabetes. If you have gestational diabetes, your blood sugar can become too high, which in turn will create a number of health risks for your baby.
The Health Of Your Baby And Gestational Diabetes In the case of your blood sugar remaining consistently elevated during pregnancy, the excess sugar can pass through your womb to your unborn baby. This can enhance your child’s future risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes. Other health risks associated with gestational diabetes include:

Jaundice Jaundice is a yellow discoloration of your baby's skin caused by bilirubin. This is a pigment produced when red blood cells break down. A number of newborn babies have jaundice, but the condition is more widespread in babies whose mothers have gestational diabetes. Babies with jaundice may be weak and have difficulty feeding. Your baby's blood will be tested for bilirubin. There is a special light available that gets rid of the bilirubin pigment which may be used to treat your baby.
Type 2 diabetes Numerous studies show that both you and your baby retain an elevated risk of developing type 2 diabetes at some point. Type 2 diabetes, which happens to be the most widespread form of diabetes, is typically caused by insulin resistance that prevents your body from using glucose properly. As a matter of fact, being overweight increases the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Hypoglycemia Under the circumstance that your unborn baby is exposed to high blood sugar levels while in the womb, the baby will eventually produce extra insulin on its own to deal with the excess sugar. This flood in insulin can then cause the baby's glucose to drop sharply right after birth, a condition called "hypoglycemia." This is an unwanted scenario. Low blood sugar is dangerous because your baby depends almost exclusively on glucose for energy at the time of birth.
Health Wellbeing Diet Fitness Diseases Nutrition
Symptoms and signs of hypoglycemia include seizures, sluggishness, and difficulty breathing. Doctors will monitor your baby's blood glucose right after birth for this simple reason. In the case that the glucose level is low, your baby will be given a sugar solution until the blood levels stabilize.
Macrosomia Macrosomia is a term that simply means "big baby" and applies to any baby whose birth weight is above 8 pounds, 13 ounces. Babies with macrosomia can experience difficulties during the childbirth process. The most familiar predicament that big babies encounter is damage to the nerves and muscles in their shoulders during vaginal delivery. Doctors will usually monitor the size of your baby by performing ultrasound exams throughout your pregnancy. If your doctor is concerned about the size of your baby, a Caesarean section may be recommended.
We Are Helping 1000 Businesses Amplify Their Online Presence
What Are The Long-Term Effects Of Gestational Diabetes On Your Baby
Babies who are born to mothers with gestational diabetes are at risk for being overweight, developing type 2 diabetes in the future, and may have some increased risk of learning difficulties.
What You Can Do For a healthy lifestyle during pregnancy, it is ideal to maintain an appropriate weight gain, average consumption of various foods from different food groups, timely and prescribed vitamin and mineral supplementation, and lots of fluid intake. Sweets and fats should also be kept to a minimum level of consumption. The following are just some of the guidelines that pregnant women with diabetes can use to achieve healthy pregnancy despite the chronic disease.
1. Follow the appropriate meal plan religiously. More than ever, pregnant women should pay attention to what they eat and their eating patterns in general. This is very important because this stage—pregnancy itself—requires strict control of blood glucose levels in order to ensure that both the mother and baby are getting the right amount of key nutrients needed.
In coming up with the right diet plan, it is best to seek the help of diabetes educator or a licensed dietitian to create the necessary adjustments needed to accommodate the needs not only of the fetus inside the womb but of the mother as well. In your meal plan, take note of calorie, carbohydrates and protein requirements every day because these will help you maintain normal blood glucose levels.
2. Regular Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose or SMBG. Experts say that the only way to tell if the woman is successful in controlling her blood glucose is by monitoring their levels themselves regularly. Since being pregnant is a sensitive condition, soon to be mothers should monitor their blood glucose levels more frequently. Ideally, SMBG should be monitored four to 10 times a day.

3. Knowledge in administering insulin injections and adjusting the doses based on the results of SMBG. Sufficient supply of insulin is very crucial for pregnant women so they must know how to administer insulin injections by themselves in case no one is around when they need it. They should also ask from their physician how to adjust the doses of insulin after they are through with the SBMG. Knowing how to adjust the doses of insulin needed is very important to ensure that the body's supply of insulin is stable.
4. Treating or controlling hypoglycemia. Pregnant women who are diabetics are more prone to hypoglycemia because of the hormonal changes in their body. Although studies show that there are no known effects of hypoglycemia in the baby, it is best to control or treat it as soon as possible.

5. Maintaining regular set of exercise or physical activities. This is also very important for pregnant women with diabetes because through this they can reduce the risk of hypoglycemia as well as being overweight. Since it is difficult for pregnant women to do strenuous workouts, it is best to maintain the hobby of having light exercises by keep the body active.
Browse All Our Informative Topics
InternetBusinessIdeas-Viralmarketing Home Page
Tweet
Follow @Charlesfrize